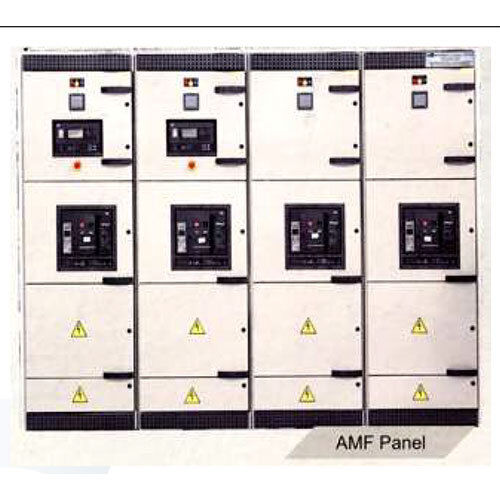
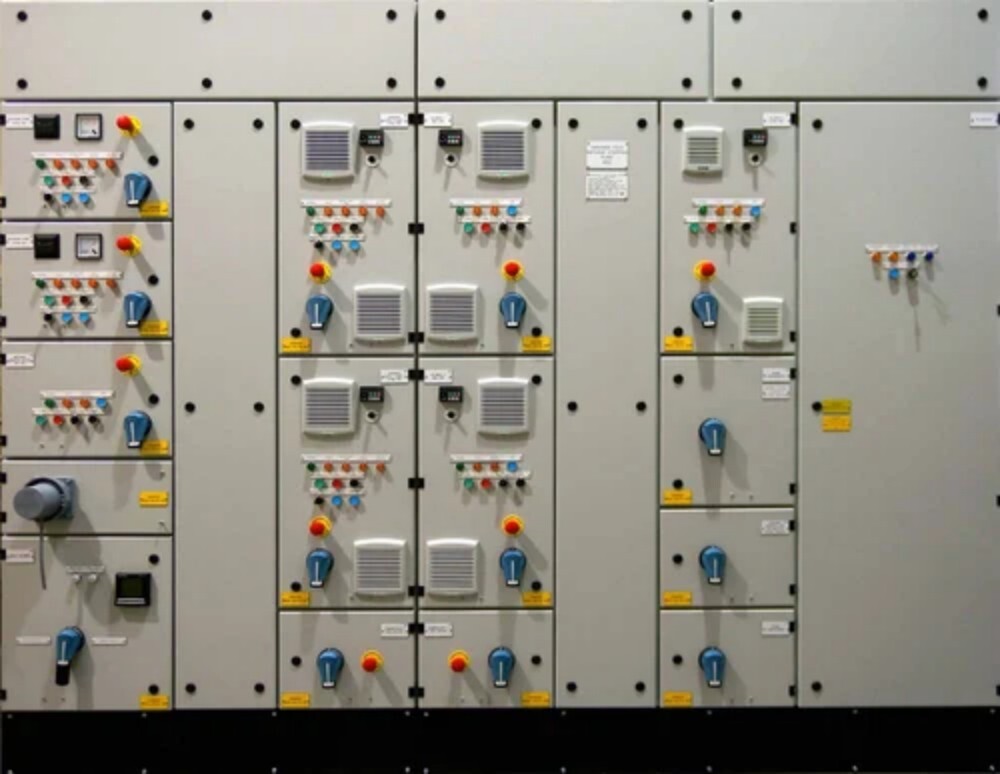
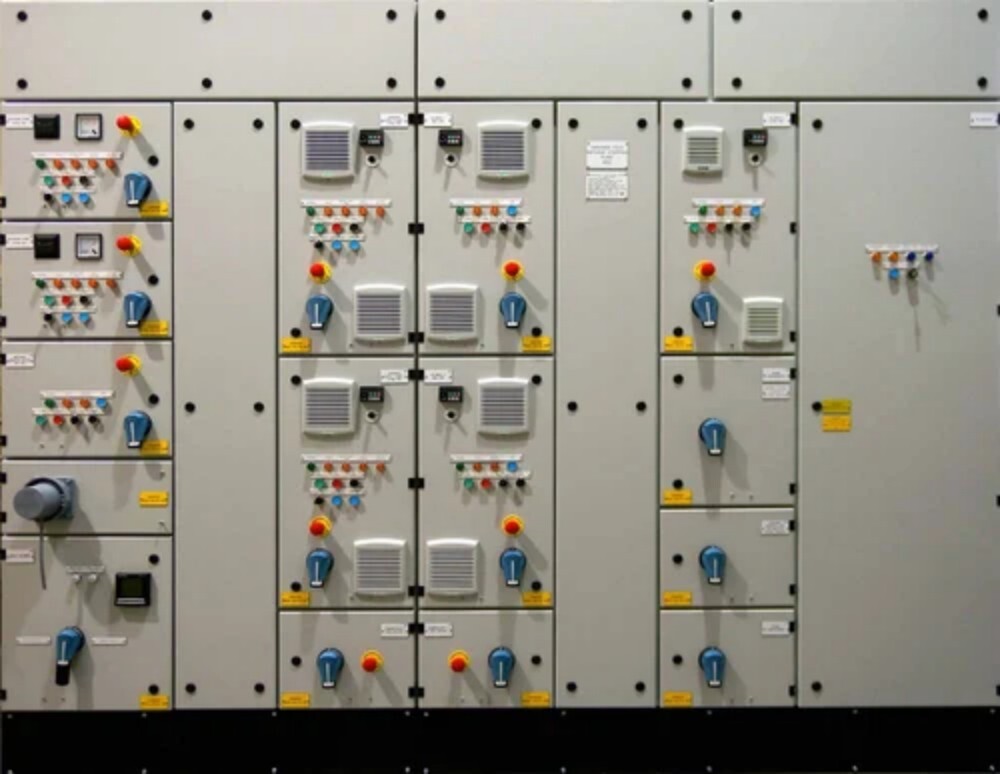
AMF Panel
AMF Panel Specification
- Rated Operation Voltage
- required based
- Cabinet Material
- required based
- Way
- required based
- Connectivity Type
- required based
- Control System
- required based
- Protection Class
- required based
- Features
- required based
- Current Rating
- required based
- Components
- required based
- Operating Voltage
- required based Volt (V)
- Thickness
- required based Centimeter (cm)
- Cooling System
- required based
- Panel Type
- required based
- Rated Current
- required based Ampere (amp)
- Base Material
- Metal Base
- Rated Insulation Voltage
- required based
- Power Rating
- required based
- Product Type
- AMF Panel
- Surface Color
- White
- Frequency (MHz)
- required based Hertz (HZ)
- Rated Voltage
- required based Volt (V)
- Usage & Applications
- required based
- Operating Temperature
- required based Celsius (oC)
- Maximum Output Current
- required based Ampere (amp)
- Cable Type
- required based
- Dimension (L*W*H)
- required based Centimeter (cm)
- Phase
- required based
- Display Type
- required based
- Material
- required based
- Conductor
- required based
- Warranty
- 1 Year
- Frequency
- required based Hertz (HZ)
AMF Panel Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Piece
- FOB Port
- NEW DELHI
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cheque
- Supply Ability
- 10 Pieces Per Week
- Delivery Time
- 7 Days
- Packaging Details
- boxes
- Main Export Market(s)
- Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About AMF Panel
An Automatic Mains Failure (AMF) panel, also known as an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) panel, is a critical component of a backup power system. Its primary function is to automatically switch the power supply from the main grid to a standby generator during a power outage and vice versa when the main power is restored. This ensures an uninterrupted power supply to critical loads.
Here's a breakdown of AMF panel specifications, functions, and components:
Functions of an AMF Panel:
- Automatic Power Source Switching: The core function is to detect mains power failure (voltage drop, frequency deviation, or complete loss) and automatically start the standby generator. Once the generator reaches the correct operating parameters, the AMF panel transfers the load from the mains to the generator. When the mains power returns and stabilizes for a set duration, the AMF panel automatically switches the load back to the mains and shuts down the generator after a cool-down period.
- Generator Monitoring and Control: AMF panels often include a dedicated generator controller that oversees various aspects of the generator's performance, such as:
- Starting and stopping the generator.
- Monitoring engine speed, oil pressure, water temperature, and fuel level.
- Providing alarms for critical parameters and faults.
- Protection Management: AMF systems are equipped to manage protection for both the generator and the mains supply, including overcurrent, over/under voltage, and earth fault protection.
- Minimizing Downtime: By automating the switch to backup power, AMF panels significantly reduce the downtime experienced during power outages, which is crucial for sensitive equipment and continuous operations.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Automating the power switch eliminates the need for manual intervention, potentially preventing data loss, equipment damage, and operational disruptions, making it a cost-effective solution in the long run.
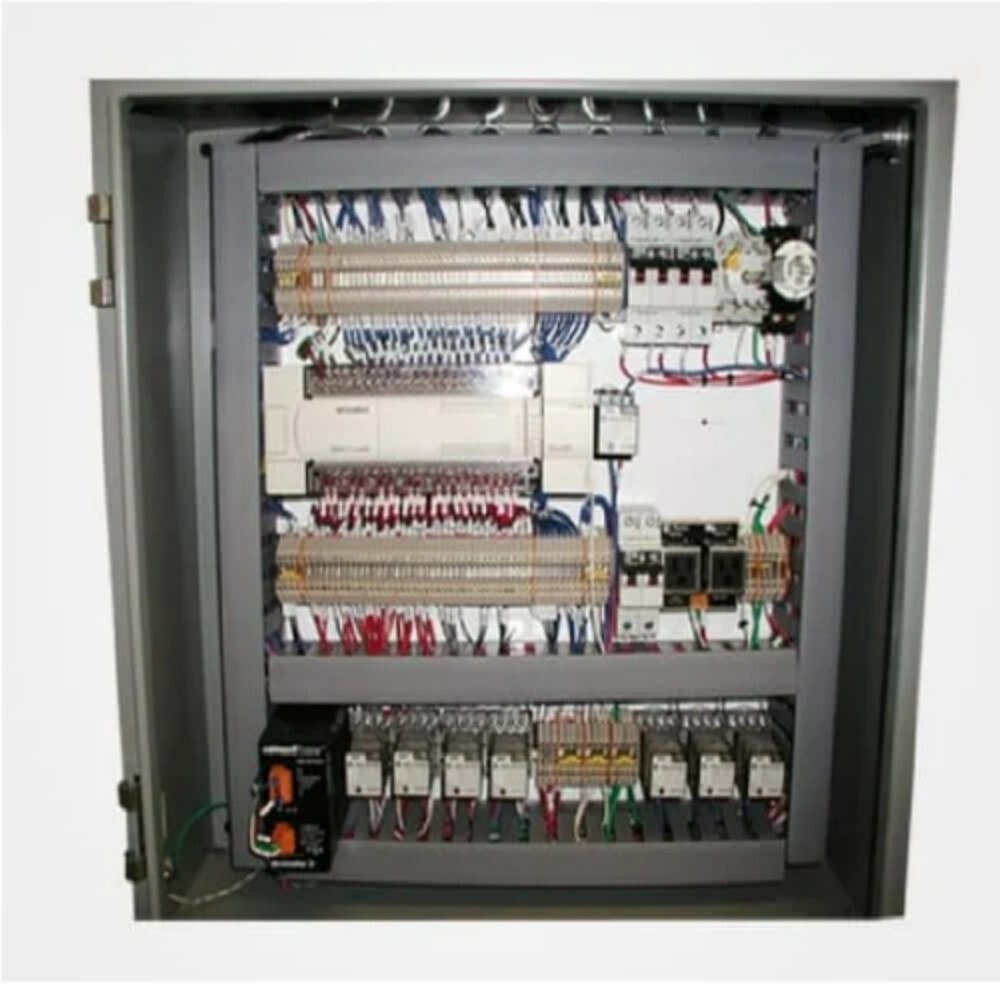
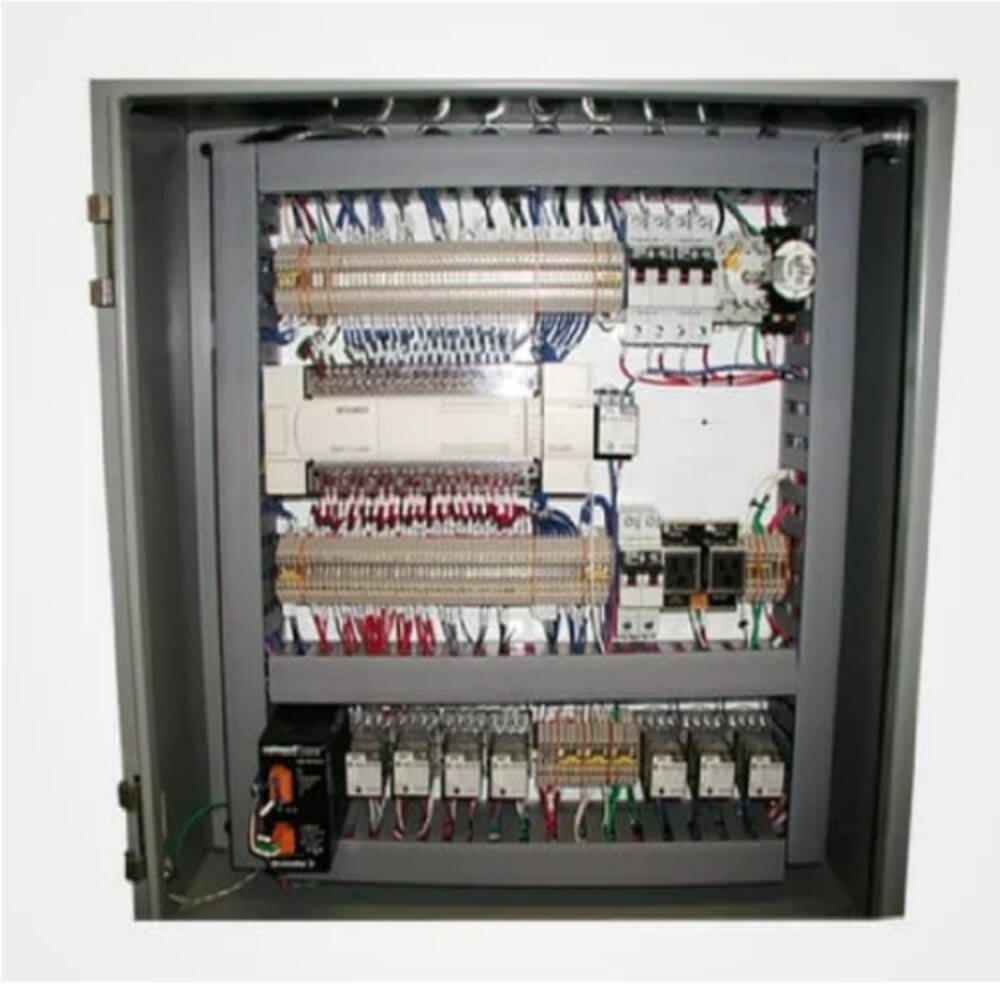
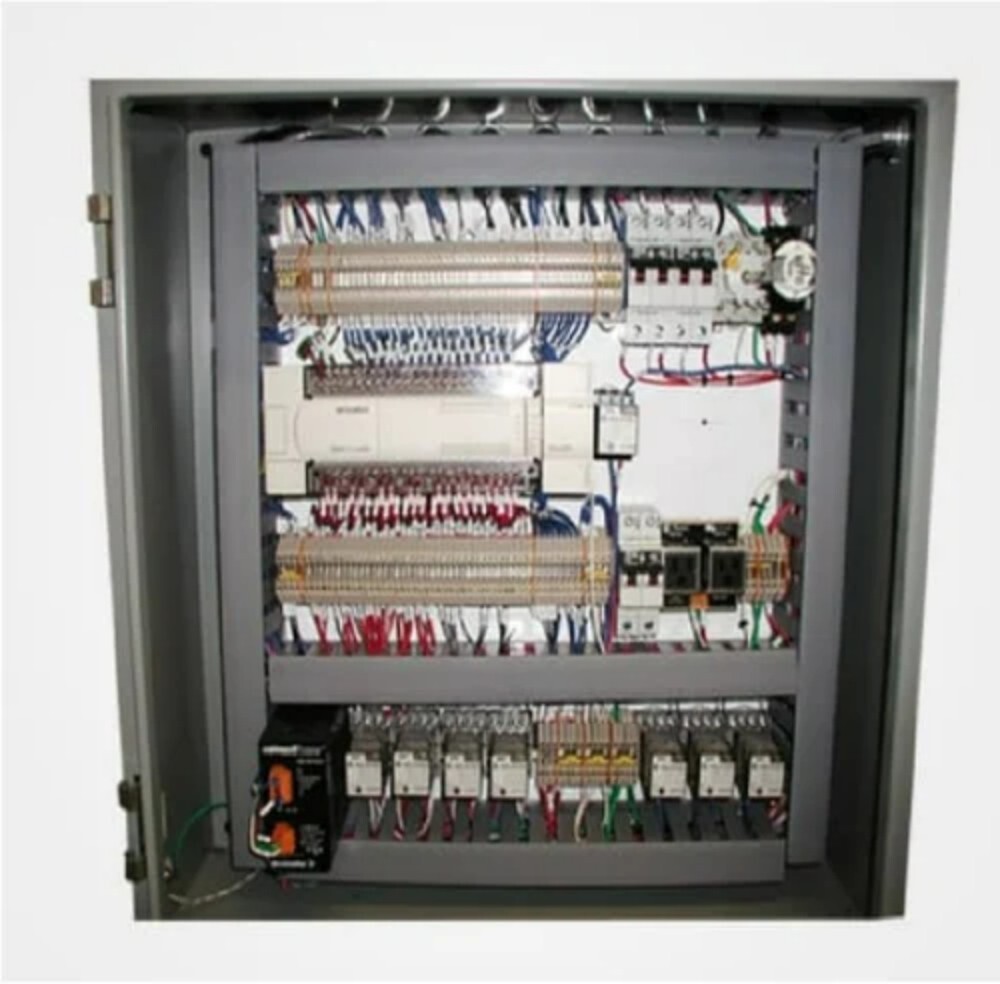
Typical Components of an AMF Panel:
- Controller (AMF/ATS Controller): This is the "brain" of the panel, responsible for monitoring the mains supply, initiating generator start/stop sequences, managing load transfer, and providing alarms. These controllers can be microprocessor-based with various programmable parameters and communication capabilities.
- Contactors or Circuit Breakers: These are heavy-duty electrical switches used to transfer the load between the mains and the generator. Mechanical interlocks are crucial to prevent the mains and generator supplies from being connected simultaneously.
- Sensing Units (Voltage, Frequency, Phase Sequence): These devices continuously monitor the parameters of the incoming mains supply to detect failures or abnormalities.
- Timers: Time delay relays are used to prevent nuisance tripping during momentary power dips and to allow the generator to warm up and cool down properly.
- Protection Devices: These include fuses, MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers), and relays (e.g., overcurrent, undervoltage, earth fault) to protect the system and connected equipment.
- Metering: Analog or digital meters (voltmeters, ammeters, frequency meters, multifunction meters) display the electrical parameters of both the mains and the generator.
- Indicating Lamps: LEDs or indicator lights provide visual status of the mains supply, generator status (running, fault), and the source of power to the load.
- Push Buttons and Selector Switches: These allow for manual operation (start/stop generator, select auto/manual mode) and testing of the system.
- Battery Charger: An automatic battery charger ensures that the generator's starting battery is always adequately charged.
- Terminal Blocks: These provide secure connection points for incoming and outgoing power cables and control wiring.
- Enclosure: A robust metallic enclosure (usually made of CRCA MS sheet or stainless steel) houses all the components and provides protection against environmental factors (dust, moisture) and electrical hazards. The IP (Ingress Protection) rating specifies the degree of protection.
- Wiring and Busbars: High-quality wiring and appropriately sized busbars (copper or aluminum) are used for power distribution and control circuits within the panel.







Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Meter Board Panel Category
PLC Panel
Price 10000 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Panel Type : required based
Rated Current : required based Ampere (amp)
Cooling System : required based
Surface Color : White





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS